In this article, you will learn how to setup SSL Certificate Authority in CentOS 7 or other Redhat based Linux OS. #centlinux #linux #ssl
Table of Contents
What is SSL Certificate Authority? :
SSL Certificate Authority, abbreviated as CA, is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the CN (Common Name) of the certificate. Third parties trust the SSL certificates of the websites that are digitally signed by a trusted CA.
Configuration of a SSL Certificate Authority (CA) Server in CentOS 7 is a simple and straight-forward operation. However, in this article, we are not only configuring a CA, besides that we are also configuring an Apache Website to use SSL Certificate and then add the root CA certificate to client’s trusted CA store.
This article focuses on a specific scenario of configuring a SSL Certificate Authority on CentOS 7 and do not addresses all the information pertains to cryptography. Therefore, it is recommended that you should read Bulletproof SSL and TLS (PAID LINK) by Feisty Duck to increase your knowledge in this area.
Environment Specification:
In this article, we are using three virtual machines with following specifications:
| Hostname: | ca-01.centlinux.com | web-01.centlinux.com | client-01.centlinux.com |
| IP Address: | 192.168.116.54 /24 | 192.168.116.51 /24 | 192.168.116.52 /24 |
| Operating System: | CentOS 7.6 | CentOS 7.6 | CentOS 7.6 |
| Purpose: | CA Server | Apache HTTP Server | Client System |
Configuring a SSL Certificate Authority in CentOS 7:
Connect to the ca-01.centlinux.com as root user by using an ssh tool like PuTTY.
Openssl package provides the necessary commands to create SSL certificates and keys.
Openssl package is by default installed on even a minimally installed CentOS 7. However, if you don’t find it then, you can install it by using yum command.
[root@ca-01 ~]# yum install -y openssl Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.ges.net.pk * epel: mirror1.ku.ac.th * extras: mirrors.ges.net.pk * updates: mirrors.ges.net.pk Package 1:openssl-1.0.2k-16.el7.x86_64 already installed and latest version Nothing to do
Openssl is already installed on this server.
For implementing public encryption, first of all, we need a private key that is later used to generate a CA certificate.
[root@ca-01 ~]# cd /etc/pki/CA/private/ [root@ca-01 private]# openssl genrsa -aes128 -out ourCA.key 2048 Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus .................................................................+++ ..............+++ e is 65537 (0x10001) Enter pass phrase for ourCA.key: Verifying - Enter pass phrase for ourCA.key:
Here, we have generated a private key using RSA algorithm with a relatively larger key size of 2048-bits for improved security.
Although, we can generate a private key without a pass phrase. But, it is strongly recommended that you should set a pass phrase while generating private keys. It increases the security during transfer or backup of the private keys.
Now create a SSL Certificate Authority (CA) certificate using the ourCA.key.
[root@ca-01 private]# openssl req -new -x509 -days 1825 > -key /etc/pki/CA/private/ourCA.key > -out /etc/pki/CA/certs/ourCA.crt Enter pass phrase for /etc/pki/CA/private/ourCA.key: You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:PK State or Province Name (full name) []:Sindh Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:Karachi Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:Ahmer's SysAdmin Recipes Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:ITLAB Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:ca-01.centlinux.com Email Address []:ahmer@example.com
Our Certificate Authority (CA) server is ready now.
Configure Apache Server to use SSL Certificates:
Connect to web-01.centlinux.com using ssh.
We have already installed Apache HTTP Server on web-01.centlinux.com. But it is running using HTTP protocol at default port 80.
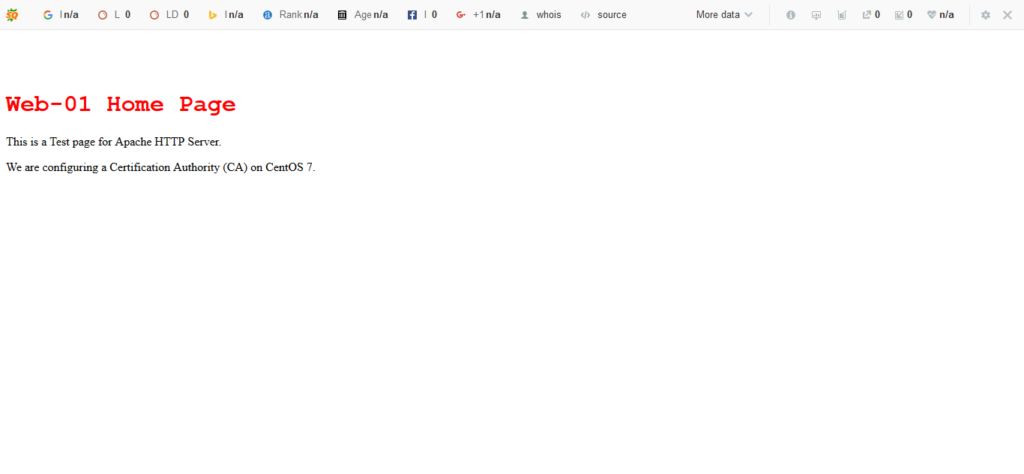
Our objective is to convert this website from HTTP to HTTPS. For this purpose, we need mod_ssl module for Apache. Therefore, we are installing it by using yum command.
[root@web-01 ~]# yum install -y mod_ssl Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.ges.net.pk * extras: mirrors.ges.net.pk * updates: mirrors.ges.net.pk Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package mod_ssl.x86_64 1:2.4.6-88.el7.centos will be installed --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ================================================================================ Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: mod_ssl x86_64 1:2.4.6-88.el7.centos base 112 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package Total download size: 112 k Installed size: 224 k Downloading packages: mod_ssl-2.4.6-88.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm | 112 kB 00:02 Running transaction check Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded Running transaction Installing : 1:mod_ssl-2.4.6-88.el7.centos.x86_64 1/1 Verifying : 1:mod_ssl-2.4.6-88.el7.centos.x86_64 1/1 Installed: mod_ssl.x86_64 1:2.4.6-88.el7.centos Complete!
During installation mod_ssl created a default configuration file ssl.conf at /etc/httpd/conf.d directory.
We can amend ssl.conf to add the SSL certificates for the website. But first we have to acquire a SSL certificate for our website.
Make sure openssl is installed on this server, because we require it to generate private key and CSR (Certificate Signing Request).
Generate a private key for the server web-01.centlinux.com.
[root@web-01 ~]# openssl genrsa -out /etc/pki/tls/private/web-01.key 1024 Generating RSA private key, 1024 bit long modulus ..................................................................................................++++++ ..++++++ e is 65537 (0x10001)
We have generated a private key with RSA key algorithm with key size of 1024.
This time we are not protecting our private key with a pass phrase, because if we set a pass phrase then whenever we start httpd.service will ask for this pass phrase.
Now, generate a CSR (Certificate Signing Request) for our website.
[root@web-01 ~]# openssl req -new -key /etc/pki/tls/private/web-01.key > -out /etc/pki/tls/web-01.csr You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:PK State or Province Name (full name) []:Sindh Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:Karachi Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:Ahmer's SysAdmin Recipes Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:ITLAB Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:web-01.centlinux.com Email Address []:ahmer@example.com Please enter the following 'extra' attributes to be sent with your certificate request A challenge password []: An optional company name []:
We have generated a CSR. Now we send it to CA for digital signature.
[root@web-01 ~]# scp /etc/pki/tls/web-01.csr root@ca-01:~/web-01.csr root@ca-01's password: web-01.csr 100% 729 353.1KB/s 00:00
Connect to ca-01.centlinux.com and digitally signed that CSR.
[root@ca-01 ~]# openssl x509 -req -in web-01.csr > -CA /etc/pki/CA/certs/ourCA.crt > -CAkey /etc/pki/CA/private/ourCA.key > -CAcreateserial > -out web-01.crt > -days 365 Signature ok subject=/C=PK/ST=Sindh/L=Karachi/O=Ahmer's SysAdmin Recipes/OU=ITLAB/CN=web-01.centlinux.com/emailAddress=ahmer@example.com Getting CA Private Key Enter pass phrase for /etc/pki/CA/private/ourCA.key:
Our CSR has been digitally signed by our SSL Certificate Authority (CA).
Transfer web-01.crt to web-01.centlinux.com.
[root@ca-01 ~]# scp web-01.crt root@web-01:/etc/pki/tls/certs/web-01.crt root@web-01's password: web-01.crt 100% 1180 1.0MB/s 00:00
Connect to web-01.centlinux.com using ssh as root user.
Now, we have a digitally signed SSL certificate. Add this certificate and private key in ssl.conf file.
[root@web-01 ~]# vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf
we only required to update following two directives therein.
SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/web-01.crt SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/web-01.key
Restart Apache service.
[root@web-01 ~]# systemctl restart httpd.service
Allow https service in Linux firewall.
[root@web-01 ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https success [root@web-01 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success
We have successfully configured our Apache server to use HTTPS protocol.
Add CA Certificate to CentOS 7 clients’ Trusted Store:
Connect to client-01.centlinux.com using ssh as root user.
Install elinks browser using yum repository.
[root@client-01 ~]# yum install -y elinks Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.ges.net.pk * extras: mirrors.ges.net.pk * updates: mirrors.ges.net.pk Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package elinks.x86_64 0:0.12-0.37.pre6.el7.0.1 will be installed --> Processing Dependency: libnss_compat_ossl.so.0()(64bit) for package: elinks-0.12-0.37.pre6.el7.0.1.x86_64 --> Processing Dependency: libmozjs185.so.1.0()(64bit) for package: elinks-0.12-0.37.pre6.el7.0.1.x86_64 --> Processing Dependency: libgpm.so.2()(64bit) for package: elinks-0.12-0.37.pre6.el7.0.1.x86_64 --> Running transaction check ---> Package gpm-libs.x86_64 0:1.20.7-5.el7 will be installed ---> Package js.x86_64 1:1.8.5-20.el7 will be installed ---> Package nss_compat_ossl.x86_64 0:0.9.6-8.el7 will be installed --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ================================================================================ Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: elinks x86_64 0.12-0.37.pre6.el7.0.1 updates 882 k Installing for dependencies: gpm-libs x86_64 1.20.7-5.el7 base 32 k js x86_64 1:1.8.5-20.el7 base 2.3 M nss_compat_ossl x86_64 0.9.6-8.el7 base 37 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package (+3 Dependent packages) Total download size: 3.2 M Installed size: 9.6 M Downloading packages: (1/4): gpm-libs-1.20.7-5.el7.x86_64.rpm | 32 kB 00:02 (2/4): nss_compat_ossl-0.9.6-8.el7.x86_64.rpm | 37 kB 00:02 (3/4): elinks-0.12-0.37.pre6.el7.0.1.x86_64.rpm | 882 kB 00:21 (4/4): js-1.8.5-20.el7.x86_64.rpm | 2.3 MB 00:55 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 60 kB/s | 3.2 MB 00:55 Running transaction check Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded Running transaction Installing : nss_compat_ossl-0.9.6-8.el7.x86_64 1/4 Installing : 1:js-1.8.5-20.el7.x86_64 2/4 Installing : gpm-libs-1.20.7-5.el7.x86_64 3/4 Installing : elinks-0.12-0.37.pre6.el7.0.1.x86_64 4/4 Verifying : elinks-0.12-0.37.pre6.el7.0.1.x86_64 1/4 Verifying : gpm-libs-1.20.7-5.el7.x86_64 2/4 Verifying : 1:js-1.8.5-20.el7.x86_64 3/4 Verifying : nss_compat_ossl-0.9.6-8.el7.x86_64 4/4 Installed: elinks.x86_64 0:0.12-0.37.pre6.el7.0.1 Dependency Installed: gpm-libs.x86_64 0:1.20.7-5.el7 js.x86_64 1:1.8.5-20.el7 nss_compat_ossl.x86_64 0:0.9.6-8.el7 Complete!
Browser URL https://web-01.centlinux.com using elinks.
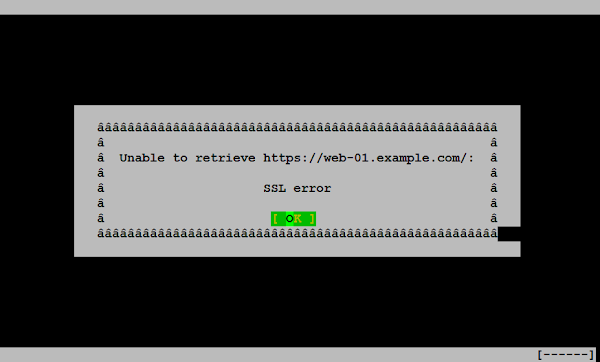
Don’t worry, we haven’t misconfigured anything. Actually this SSL error is thrown because our CA is not included in local ca-trust store of client-01.centlinux.com.
Install CA certificate by adding it to local ca-trust store. But first, we acquire the CA certificate from ca-01.centlinux.com.
[root@client-01 ~]# cd /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/ [root@client-01 anchors]# scp root@ca-01:/etc/pki/CA/certs/ourCA.crt . root@ca-01's password: ourCA.crt 100% 1476 684.7KB/s 00:00
Now, use the following command to add ourCA.crt to local ca-trust store.
[root@client-01 anchors]# update-ca-trust
Browse URL https://web-01.centlinux.com again.
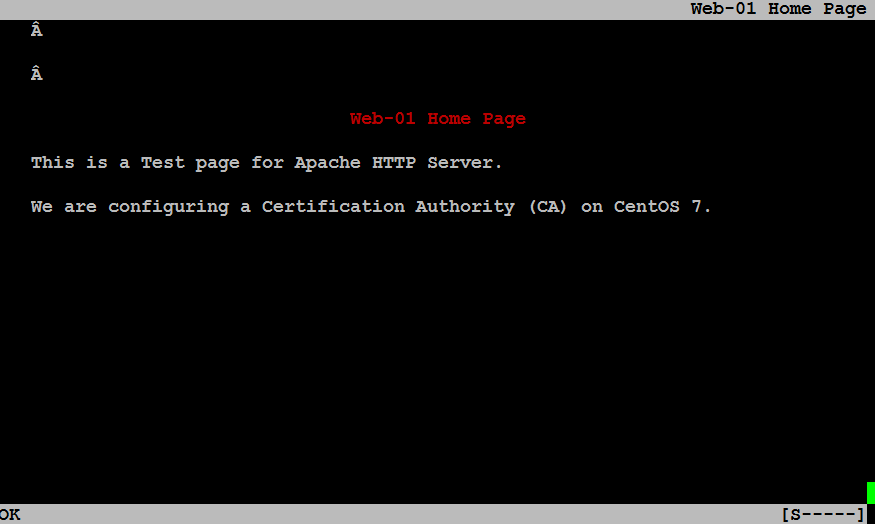
Conclusion:
In this configuration guide, we have successfully configured a SSL Certificate Authority on CentOS 7 server. You can refer to our next article, if you want to install SSL certificate on Nginx web server.

Many Thanks for this complete tutorial, I've followed all the instructions, but I'm getting an SSL error when trying to browse the website using https.
I'm able to browse http using elinks, but https is not working, I'm running Centos 7.
I've seen the following two commands on other websites/forums:
sudo update-ca-trust enable; sudo update-ca-trust extract
Are they necessary?
Thanks again.
Hi,
Thanks for appreciation.
Following steps may be executed to resolve the issue.
1) Copy ourCA.crt to /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/ on client's system.
2) execute "update-ca-trust".
Thanks for complete step by step. In my current environment just followed the steps blindly. it worked!!
Thanks for complete step by step but I face one problem i can't get green signal and show in browser yellow triangle
Check the certificate details in browser and it will give you the actual cause of the problem.
Wonderful article. I set it up with the above steps and it is working fine with Firefox. In google chrome though, I believe post version 58, I think it is necessary to add "Subject Alt Names" else we still see the dreaded "Not Secure" icon. Can you please let know how to do it?
Thanks for liking this article. You are right that CN certificates are being replaced by SAN certificates. I will try to write something on SAN Certificates a.s.a.p. But for immediate solution you can also use the same openssl command with some different switches to generate a SAN certificates as well.
Great tutorial. Can you please add how to generate intermediate certs ?
Thanks. I had already written on Self Signed Certificates several times. But I do not add the information here to kept the scope of this article to Certificate Authority only.
Perfect ! many thanks 😉
Did you write something on :
CAs ans SubCAs ?
Cross linked CAs between organizations ?
I'm looking for reliable informations on these subjects …
Have a nice week-end 😉
Thanks. We do not yet worked on the above topics. But we will try to work on it a.s.a.p.
our client are using window 10 so could you help me how to install ourca.crt on windown 10 . thank you so much!
For MS Windows, you have to add the ourca.crt in your Internet Explorer. Go to Internet Options > Content > Certificates and import ourca.crt.
Great tutorial.
So how can i revoke ssl cert?
Thanks. You can use "openssl -revoke" command for this purpose.