In this guide, you will learn how to install Squid Proxy on CentOS 7 or other Redhat based Linux OS. #centlinux #linux #squidproxy
Table of Contents
What is Squid Proxy? :
Squid is a caching and forwarding HTTP web proxy. Squid has a lot of features, and it is used in variety of situations such as speeding up web server by caching repeated requests, caching web and DNS lookups, filtering traffic, blocking websites, etc. It is written in C++ and distributed under GNU GPL license.
Squid is considered as the most reliable content control software and has been used by many organizations since last 2 decades.
In this article, we are installing Squid proxy server on CentOS 7. Although, there are too many similar articles already available on the web. But we write this article to include even the minor (but important) steps, that are usually overlooked by the other writers.
This article is strongly emphasizes on the installation and initial configuration of the Squid proxy server on CentOS 7. Therefore, if you are willing to configure some advance settings in Squid proxy then we strongly recommend you to purchase Squid Proxy Server 3.1: Beginner’s Guide (PAID LINK) by Packt Publishing.
Environment Specification:
We have provisioned a CentOS 7 virtual machine with following specification.
- CPU – 3.4 Ghz (1 Core)
- Memory – 1 GB
- Storage – 20 GB
- Operating System – CentOS 7.7
- Hostname – squid-proxy-01.example.com
- IP Address – 192.168.116.214/24
Install Squid Proxy on CentOS 7:
Connect with squid-proxy-01.example.com using ssh as root user.
Squid software package is available in standard yum repositories, therefore, we are installing Squid proxy using yum command.
# yum install -y squid
Enable and start Squid proxy service.
# systemctl enable --now squid.service Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/squid.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/squid.service.
Allow Squid proxy service in CentOS 7 firewall.
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=squid success # firewall-cmd --reload success
Configure Squid Proxy on CentOS 7:
Global configuration file for Squid web proxy is /etc/squid/squid.conf. We can customize it according to our requirement.
# vi /etc/squid/squid.conf
Add following directives therein.
dns_v4_first on
Restart Squid proxy service to load changes.
# systemctl restart squid
Configure Client’s Browser to use Squid Proxy Server:
Start the client browser and add our Squid proxy in its settings.
To do this, open Internet Explorer and go to Internet Options.
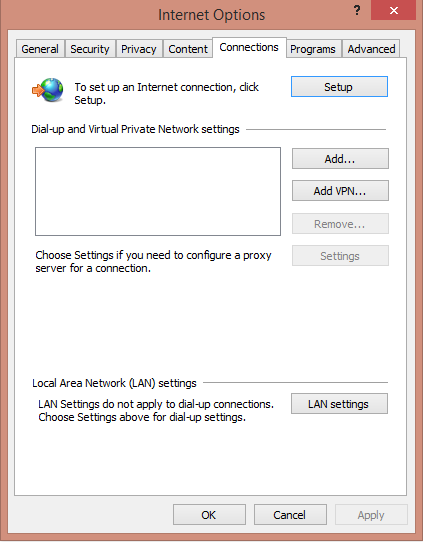
Go to Connections Tab and click on LAN settings.
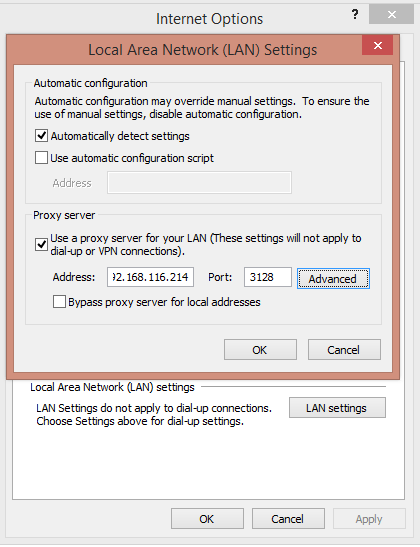
Enter Squid Proxy IP Address and Port in the above dialog box.
Click on OK to exit from Internet options.
Browse https://centlinux.com in Internet Explorer.
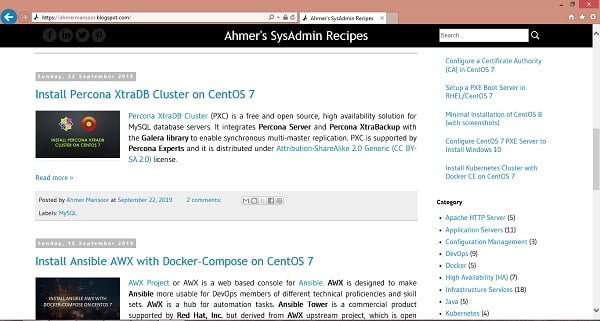
The above website has been served through our Squid proxy server.
Configure Squid Client Authentication:
We can use HTTP basic authentication to configure user based authentication for Squid proxy server.
Install httpd-tools package using yum command.
# yum install -y httpd-tools
Create the password file and add squiduser user therein.
# htpasswd -c /etc/squid/passwd squiduser New password: Re-type new password: Adding password for user squiduser
Change owner of the passwd file.
# chown squid.squid /etc/squid/passwd
Now, edit Squid configuration file and add Client authentication settings.
# vi /etc/squid/squid.conf
Add following directives after the ports’ ACLs.
auth_param basic program /usr/lib64/squid/basic_ncsa_auth /etc/squid/passwd auth_param basic children 5 auth_param basic realm Squid Basic Authentication auth_param basic credentialsttl 2 hours acl auth_users proxy_auth REQUIRED http_access allow auth_users
Restart Squid proxy service to take changes into effect.
# systemctl restart squid
Open URL https://centlinux.com in the web browser.
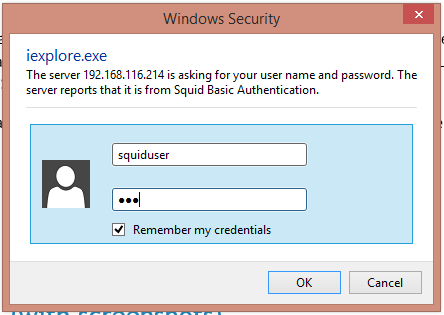
This time, it is prompting for the authentication.
Creating a custom Blacklist to block websites:
Create a blacklist file to block websites.
# vi /etc/squid/blacklist
and add following URLs therein.
.yahoo.com .facebook.com
Edit Squid proxy configuration file to add blacklist settings.
# vi /etc/squid/squid.conf
add following directives after the ports’ ACLs.
acl bad_urls dstdomain "/etc/squid/blacklist" http_access deny bad_urls
Restart Squid proxy service to load changes.
# systemctl restart squid
Open URL http://www.yahoo.com in a web browser.
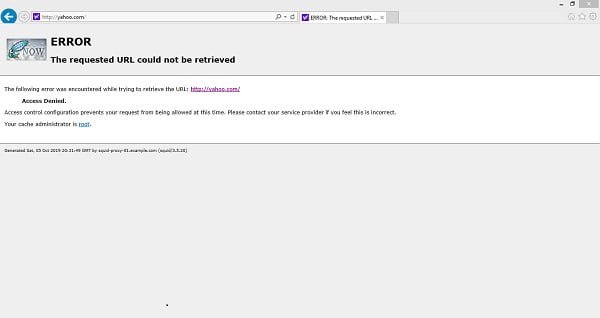
You can see that the http://www.yahoo.com has been blocked by our Squid proxy server.
Conclusion:
In this guide, you have learned how to install Squid Proxy on CentOS 7 or other Redhat based Linux OS.
