Learn how to install Certificate Authority server on Rocky Linux 9 with our comprehensive guide. Secure your network and enable encrypted communication efficiently with step-by-step instructions and best practices. #centlinux #linux #cryptography
Table of Contents
What is a Certificate Authority Server?
Certificate Authority Server or CA Server is like a digital security guard for the internet. It issues SSL/TLS digital certificates, which are virtual ID cards for websites or online services. These certificates verify the identity of the website and help create a secure connection between your device and the website, ensuring that your information stays safe during online communication.
Common Certificate Authority software includes:
- Let’s Encrypt: This is a widely used and free certificate authority that helps websites secure their connections.
- DigiCert: A well-known commercial CA Server that provides SSL and other digital certificates to enhance online security.
- Entrust Datacard: This Certificate Authority offers various digital security solutions, including certificates for websites and online transactions.
- Comodo CA: Another provider that offers digital certificates and cybersecurity solutions to protect online communications.
Using a Certificate Authority is essential to maintain a secure and trustworthy online environment.
What does a Certificate Authority do?
A Certificate Authority (CA) is responsible for issuing digital certificates that authenticate the identity of entities on a network. These certificates are used to establish secure communication channels by encrypting data transmitted over the internet. Additionally, CAs verify the legitimacy of websites and ensure that data exchanges between parties are protected from unauthorized access or tampering.
What is Dogtag Certificate System?
Dogtag Certificate System, commonly referred to as Dogtag CA, is an open-source Certificate Authority software suite. It provides a set of services for managing and issuing digital certificates within an enterprise or organization. The Dogtag Certificate System is designed to meet the security and certificate management needs of large-scale deployments.
Key features of Dogtag CA include:
- Certificate Management: It facilitates the issuance, renewal, and revocation of digital certificates, which are crucial for establishing secure communication channels.
- Key Pair Generation: The system can generate and manage cryptographic key pairs used in the creation of digital certificates.
- LDAP Integration: Dogtag CA often integrates with LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) for efficient and scalable directory services.
- Smart Card Support: It supports the use of smart cards for enhanced security in authentication and certificate management.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): Dogtag CA is part of a PKI, which is a framework that manages digital keys and certificates.
Dogtag Certificate System is commonly used in enterprise environments where a robust and secure certificate management system is required. It’s particularly well-suited for organizations that need to manage a large number of digital certificates and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of their communication channels. The open-source nature of Dogtag CA allows for flexibility and customization to meet specific organizational requirements.
Environment Specification:
We are using a minimal Rocky Linux 9 virtual machine with following specifications.
- CPU – 3.4 Ghz (2 cores)
- Memory – 4 GB
- Storage – 40 GB
- Operating System – Rocky Linux release 9.2 (Blue Onyx)
- Hostname – ca-server.centlinux.com
- IP Address – 192.168.18.83/24
Prepare your Certificate Authority Server:
Login to your Rocky Linux Server as a privileged user by using any ssh client.
Set hostname for your Linux machine and configure local DNS resolution as follows.
# hostnamectl set-hostname ca-server.centlinux-com.preview-domain.com # echo 192.168.18.83 ca-server ca-server.centlinux-com.preview-domain.com >> /etc/hosts
To install Dogtag CA, you must increase the maximum number of file descriptors that your system can open at a time.
# vi /etc/security/limits.conf
Add following lines in this file.
# Dogtag CA Settings root hard nofile 4096 root soft nofile 4096
Update Linux software packages by executing following command.
# dnf update -y
The above command may also update software packages related to Linux Kernel. In such case, reboot your Linux machine before moving forward.
# reboot
Check the Linux OS & Linux Kernel versions.
# cat /etc/os-release | grep PRETTY_NAME PRETTY_NAME="Rocky Linux 9.2 (Blue Onyx)" # uname -r 5.14.0-284.30.1.el9_2.x86_64
Recommended Training: Linux Command Line

Install Certificate Authority Server: Dogtag CA
Dogtag certificate server requires LDAP database for storing certificate and user information. Therefore, you should install LDAP server along with your Certificate Authority software.
# dnf install -y 389-ds-base pki-ca
Create a file ~/instance.cfg to configure LDAP Directory Server (DS) instance.
# vi ~/instance.cfg
Add following lines in this file.
[general]
config_version = 2
[slapd]
root_password = Ahmer@1234
[backend-userroot]
sample_entries = yes
suffix = dc=ca-server,dc=centlinux,dc=com
You can now use dscreate command with instance.cfg file to create directory server instance.
# dscreate from-file ~/instance.cfg Starting installation ... Validate installation settings ... Create file system structures ... Create self-signed certificate database ... Perform SELinux labeling ... Create database backend: dc=ca-server,dc=centlinux,dc=com ... Perform post-installation tasks ... Completed installation for instance: slapd-localhost
Execute pkispawn command to create your Certificate Authority Server.
# pkispawn
IMPORTANT:
Interactive installation currently only exists for very basic deployments!
For example, deployments intent upon using advanced features such as:
* Cloning,
* Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC),
* External CA,
* Hardware Security Module (HSM),
* Subordinate CA,
* etc.,
must provide the necessary override parameters in a separate
configuration file.
Run 'man pkispawn' for details.
Subsystem (CA/KRA/OCSP/TKS/TPS) [CA]:
Tomcat:
Instance [pki-tomcat]:
HTTP port [8080]:
Secure HTTP port [8443]:
AJP port [8009]:
Management port [8005]:
Administrator:
Username [caadmin]:
Password:
Verify password:
Import certificate (Yes/No) [N]?
Export certificate to [/root/.dogtag/pki-tomcat/ca_admin.cert]:
Directory Server:
Hostname [ca-server.centlinux.com]:
Use a secure LDAPS connection (Yes/No/Quit) [N]?
LDAP Port [389]:
Bind DN [cn=Directory Manager]:
Password:
Base DN [o=pki-tomcat-CA]:
Security Domain:
Name [ca-server.centlinux.com Security Domain]:
Begin installation (Yes/No/Quit)? Yes
Installing CA into /var/lib/pki/pki-tomcat.
==========================================================================
INSTALLATION SUMMARY
==========================================================================
Administrator's username: caadmin
Administrator's PKCS #12 file:
/root/.dogtag/pki-tomcat/ca_admin_cert.p12
To check the status of the subsystem:
systemctl status pki-tomcatd@pki-tomcat.service
To restart the subsystem:
systemctl restart pki-tomcatd@pki-tomcat.service
The URL for the subsystem is:
https://ca-server.centlinux.com:8443/ca
PKI instances will be enabled upon system boot
==========================================================================
Enable pki-tomcatd.target, to ensure autostart of Dogtag service.
# systemctl enable pki-tomcatd.target Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/pki-tomcatd.target → /usr/lib/systemd/system/pki-tomcatd.target.
Reboot your Rocky Linux machine.
# reboot
Post-installation Configuration:
File instance.cfg contains the root password in plain text. Since this file is no longer required, therefore, premanently delete the this file by using shred command.
# shred -u -z ~/instance.cfg
Dogtag web interface uses service port 8443/tcp. Therefore, to make your Certificate Authority server accessible across the network, you need to enable this port in your Linux Firewall.
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8443/tcp success # firewall-cmd --reload success
Open URL https://ca-server.centlinux.com:8443/ in a web browser.

You will encounter a Certificate Warning in your Web Browser. It is because the SSL certificate of your CA server is self signed and your browser does not see your CA server as trusted.
Click on <ENTER>.

Click on <Certificate Authority>.

Click on <SSL End Users Services>.
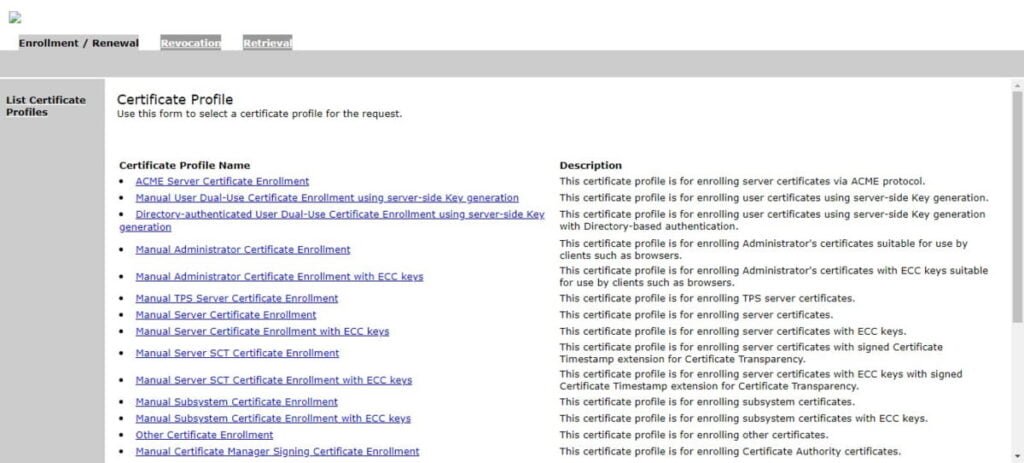
Due to the SSL certificate error, your web browser display warnings for SSL agent. To get rid of these warnings, you need to import your root CA certificate in your web browser.
If you are accessing Dogtag web interface from a Linux machine then you can install your root CA certificate by using scp command.
# scp /root/.dogtag/pki-tomcat/ca_admin_cert.p12 ahmer@web-01.centlinux.com:
For windows machine, you can use an sftp client to install root CA certificate to your client. Or in Windows 11, you can use pscp native command to do the same.
> pscp root@ca-server:/root/.dogtag/pki-tomcat/ca_admin_cert.p12 . root@ca-server's password: ca_admin_cert.p12 | 2 kB | 2.9 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100%
You can now import root CA certificate in your web browser.
Refresh the Dogtag web interface.
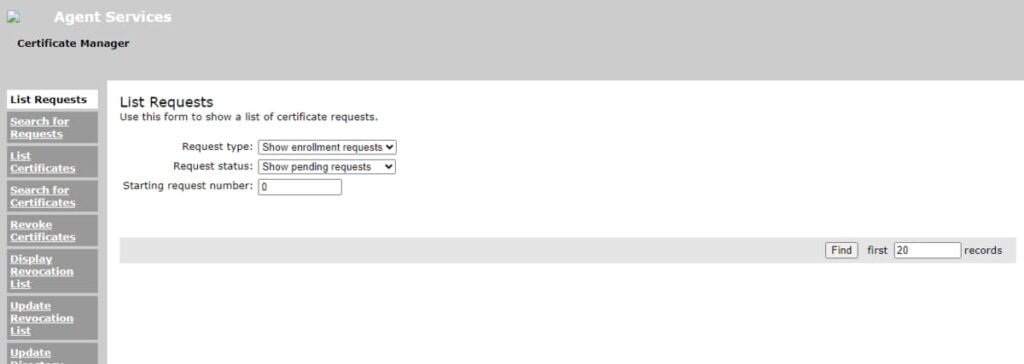
Your free Certificate Authority Server has been configured successfully.
Read Also: Setup Certificate Authority Server in CentOS 7
Video Tutorial to Setup Dogtag Certificate System:
Final Thoughts
Install Certificate Authority server on Rocky Linux 9, is a crucial step in enhancing the security of your network infrastructure. By setting up a CA, you can issue digital certificates that authenticate the identities of entities and enable encrypted communication, safeguarding sensitive data from potential threats. Understanding the role of SSL/TLS protocols in securing communication further solidifies the importance of implementing robust encryption measures. With careful planning and adherence to best practices, you can establish a strong foundation for secure network communication, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data exchanged across your network.
In this Linux tutorial, you have learned how to configure a in-premises CA server on CentOS/Rocky Linux by using Dogtag CA software. We recommend that to understand cryptography. you should read Bulletproof TLS and PKI, Second Edition: Understanding and Deploying SSL/TLS and PKI to Secure Servers and Web Applications 2nd ed. Edition (PAID LINK) by Ivan Ristic.

